Solutions to ABS 3D Printing
Even though ABS faces multiple challenges, solving them is definitely possible. With careful consideration and proactive measures, the challenges can be easily overcome. We help you with a list of problems and factors to consider while printing with ABS material.
First we need to understand ABS material properties.
FDM ABS MATERIAL PROPERTIES
TECH SPECS
- Heat Deflection (ASTM 648, 66 psi) 210°F 99°C
- Flexural Modulus (ASTM D790, 15 mm/min) 377,000 psi 2,600 MPa
- Tensile Strength at yield (ASTM D638, 50 mm/min) 0.806 psi 43 MPa
- Tensile Modulus (ASTM D638, 50 mm/min) >348,000 psi >2,400 MPa
- Strain at Yield – Elongation (%) >5.6% >5.6%
- Notched Impact Strength (ASTM D256) >3.6 ft-lb/in >192 J/m
- (Specifications for MakerBot ABS)
GUIDELINES TO ABS 3D PRINTING
Ideal Extrusion Temperature Range
It is important for users to always print ABS within the ideal or recommended temperature range. The temperature range is provided by the filament manufacturer and the entire range should be explored for the ideal temperature for your 3D printer and the environment you are working in. For METHOD the extruder temperature for ABS is 245°C.
Heated Build Plate vs Heated Build Chamber
Due to ABS’s rate of shrinkage while cooling, it is strongly recommended that a heated build chamber is used when printing. This will allow the print to maintain an elevated temperature until the job is complete, at which point the entire print is able to cool at a constant rate ensuring dimensional accuracy and structural integrity are maintained. If a heated chamber is not an option, another less ideal option is to use a heated build plate with an enclosure. The heat on the build plate will increase adhesion while the enclosure will attempt to mimic a heated chamber. Note that for the second configuration, the part’s accuracy and strength will decrease as the part’s size increases.
Real ABS vs Modified ABS
There are many formulations of ABS and depending on what type of 3D printer you have access to, you may elect to choose a variety that has been modified to favor less curling. These modifications tend to have a negative impact on material properties so ensure you know what you are getting before you purchase. If your goal is to closely mimic ABS used in injection molding, you’ll want to stick with the least modified version of ABS you can find. Remember, real ABS will require a heated build chamber to print well.
Ventilation
ABS 3D printing should always be carried out in a well ventilated room. Typically an open office environment with industrial HVAC should do the trick.
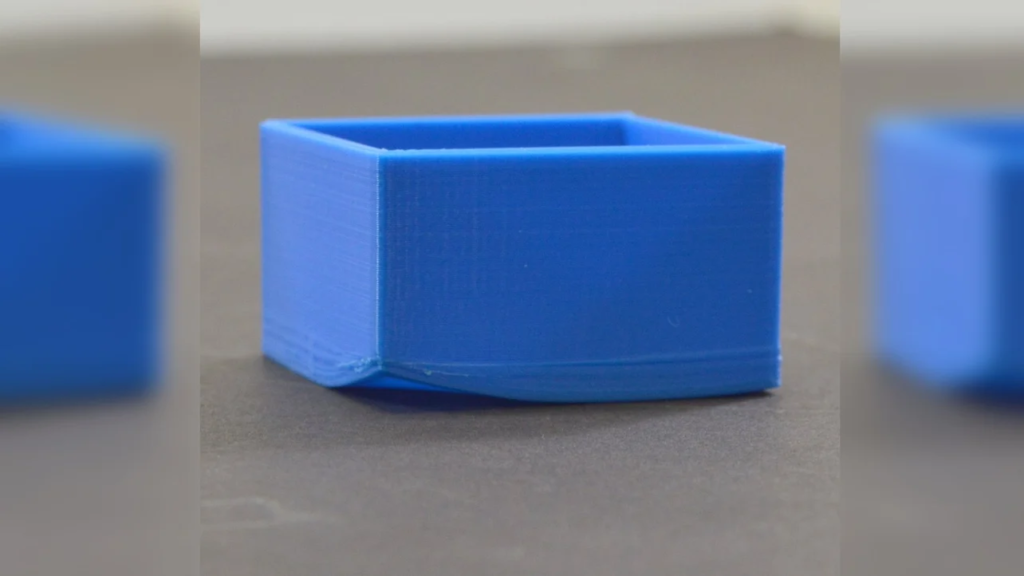
Warping, Curling & Cracking
Warping, curling & cracking can be big problems in ABS 3D printing. If not controlled, the print can warp, curl, or even crack after a few layers. These problems are visible only after some printing is done and so the print has to be constantly monitored to make sure the print is running perfectly. To reduce the chances of Warping, Curling & Cracking users have to take certain precautions as mentioned below.
First Layer Adhesion
Users should ensure that the first layer of the print has sufficient adhesion. The first layer adhesion can be controlled through multiple means like using a heated bed or a heated chamber. Both these features are important for ABS printing and help in keeping the printed part well heated. The heat prevents the layers from completely solidifying, thus avoiding warping or cracking.
Using Gluing agent
To increase the first layer adhesion, users can apply glue to the print bed. They can either use a regular glue stick, or specially formulated Magigoo adhesive or use ABS slurry.
ABS Slurry : It is a mixture of ABS filament pieces mixed with acetone. The mixture forms a thick gooey substance that is spread over the print bed to act as a glue. Take adequate care while creating this mixture.
Using Bed Adhesion Tools
Users can also try to control the warping and cracking issues through slicer settings. Slicer softwares have bed adhesion tools like raft and brim. These can significantly improve the first layer adhesion of the print.
Raft: Raft is a horizontal structure over which the entire part is 3D printed. Its sole purpose is to increase the surface area in touch with the bed.
Brim: The brim is similar to a raft but a brim only extends from the outer surface of the print. It has no contact with the print’s underside.
Tweak Slicer Settings
Other slicer settings that can help in increasing the bed adhesion are fan settings. Fans can be either run at low speeds for the entire duration of the print or else simply switched off while printing with ABS. This will help in keeping the print warm and in a heated state to improve bed adhesion.
advantages
➜ Manufacturing-Grade Material: ABS filament offers great mechanical properties like strength, ductility, impact, and wear resistance. This makes it an important manufacturing-grade material
➜ Easy to Post-Process: ABS can be machined, polished, sanded, filed, drilled, painted, glued, etc. with extreme ease, and the finish is still good.
➜ Wide-Ranging Applications: It has wide ranging applications in prototyping, especially for aesthetic prototypes and end-use parts as well.
DISADVANTAGES
➜ Warping, Curling & Cracking: ABS is highly prone to warping, curling & cracking. Without necessary precautions, the print will fail.
➜ Advanced Feature Requirements: ABS is a demanding material and it requires multiple features to ensure it is successfully printed. For most hobbyist and even professional level 3D printers, ABS will produce inconsistent results, while traditional industrial 3D printers can be out of reach due to high costs. Next generation desktop 3D printers such as the MakerBot METHOD are changing this with industrial features designed to control the 3D printing environment and produce consistent results while still being affordable.
WHERE TO BUY?
ABS material can either be bought from filament manufacturers or 3D printer manufacturers. For the MakerBot METHOD, we recommend use of MakerBot ABS as it is optimized to deliver great results.
Looking for a professional 3D printing platform that works with a variety of manufacturing-grade materials? Learn more at makerbot.com/method.
A Note to MakerBot METHOD Users Printing ABS:
The above guide is intended to discuss the challenges and techniques for printing ABS with a variety of desktop 3D printers. METHOD is designed to print real ABS without modification or special settings thanks to its unique environmental regulation features such as the heated build chamber. It is recommended to use optimized ABS settings within MakerBot Print for best results.